|
|
|
|||
|
|
||||
|
|
||||
| Plan: Jetex Job | ||||
|
|
HOME | SITE MAP | FORUM | CONTACT |
|
||
|
ABOUT | MOTORS | MODELS | ARCHIVE | HISTORY | STORE | FAQ | LINKS
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
Jetex Job
by Henry Struck Reprinted from Air Trails Pictorial, February 1949, pp. 65ff. THE NEW ENGLISH SOLID FUEL JETEX ENGINE OPENS UP NEW AVENUES OF EXPERIMENTATION FOR MODEL PLANE DESIGNERS |
|
||||||||||||||
|
ANYONE who has thrilled to the smooth, rushing flight of a jet fighter and longed for similar power for his models should find the new British Jetex units of special interest. The Jetex is actually a rocket-type engine, since the oxygen required to support combustion is contained within a solid fuel charge which is ignited within the container. There are no moving parts and only the lighting of a plastic fuse is necessary to set the "engine" in action. Considered quite safe in operation, the Jetex has a spring-loaded cover to permit the gases to escape should the jet exit become clogged. The fuel itself does not continue burning in the open air when lighted with a match. Radically new and exciting designs are possible with this power supply. The reduction of drag assumes prime importance, as the ratio of the exhaust velocity to the model velocity determines the efficiency at which the motor is operating. Weight must be kept at a minimum, to permit the model to accelerate rapidly, without wasting the thrust available. The Jetex unit fits neatly into the idea of a low-drag design. A pusher installation produces a sleek fuselage, with the small engine diameter of one inch fully cowled, provided cooling airflow over the unit is maintained. The absence of a propeller eliminates the long landing gear problem, as well as the breakage of propellers and the business of wearing one's fingers out twisting them. The lack of torque simplifies control, especially in tailless designs, while the constant and equal thrust obtained from each charge makes twin-engine types practical. Only a few simple steps are necessary to operate the Jetex unit. Remove it from the model, where it may be mounted either on a single screw or in a spring clip-both of which are furnished with the engine. Snap off the cover and drop a charge into the case. Press the coiled plastic wick against the top of the charge with the disc of wire mesh (a supply of wicks and circular meshes comes with the engine). Replace the cover and replace the unit in the ship. Light the wick (with a cigarette or match) and hold the model in flight attitude. There is no need for haste since several seconds are necessary for the fuel to generate full pressure. This moment is indicated by a steady hissing sound, and model is launched. No batteries, props, cranking or pumping. No fuel dripping off your elbow. No screaming and roaring. The ship illustrated was designed to test the ability of the Jetex unit, rather than to achieve the ultimate in performance. It is built to nearly the maximum weight of 3 ounces specified by the engine manufacturer. Sensitive to the slightest adjustment, it has turned in many excellent flights. Upon being launched in the conventional manner – not hurled into the air – the model gathers speed steadily and climbs swiftly throughout the engine run of 20 seconds. The compact design can absorb much punishment without damage and is extremely simple to construct. The wing is built first. It is a straight taper with 37° of sweepback, which is the equivalent of about 7° of dihedral. Lay out the planform on a flat surface to the dimensions given on the drawings. Mark off the tips in ¼" squares and plot the outline. Shape the leading edges from a pair of soft balsa strips Select a soft block of balsa 1¾" × 2" × 7¼" for the fuselage. Lay out the top and side views on the block using the ¼" squares to obtain the necessary dimensions. Shape the fuselage from a flat topped section under the wing, to a rounded section at the nose. Hollow out the block to a thickness of about Sand the entire ship carefully to remove any bumps that might spoil the finish. Apply a couple of coats of clear dope and sand smooth. Cover the wing with light tissue, spray with water and dope when dry. Screw the Jetex unit in place and balance the model. Add ballast to the nose if necessary to bring the C.G. 7¼" from the front. Glide the model, launching it smartly. Adjust any tendency to stall by bending down the trailing edge, or to dive by bending up the trailing edge. Spiralling can be controlled by bending up the trailing edge of the wing tip on the outside of the turn. To correct a left spiral bend up the right tip, and vice versa. Only a slight amount of adjustment is required, due to the high speed and the sensitivity of the controls. Make the first flights with the solid fuel charges sawed in half, making further adjustments to the trailing edge if necessary to obtain a wide climbing circle. When the model is flying smoothly under full charge, a cowl formed of Without the usual elaborate process required to install the power plant, the Jetex may be quickly shifted from one model to another. |

-
Air Trails Pictorial, Feb. 1949 (p. 66)
The illustration below appeared as an inset to the plan, to familiarise readers with the size and appearance of the new motor and its fuel. 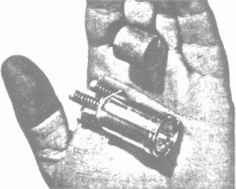
- Air Trails Pictorial, Feb. 1949 (p. 67)
|
||||||||||||||
Plan for Jetex Job
(A larger copy of the plan is also available to
view or download). |
|||||||||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Acknowledgements - Article and plan from the MAAC archives, via Bill Henderson |
|
|
|
|
ABOUT | MOTORS | MODELS | ARCHIVE | HISTORY | STORE | FAQ | LINKS |
|
|
Terms of Use
|
Queries? Corrections? Additions?
Please
contact us.
|
|